Bufotenin
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | N,N-dimethyl-5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-hydroxy-dimethyltryptamine, bufotenine, cebilcin |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.971 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
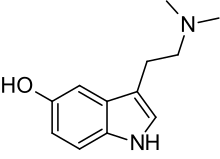
| Formula | C12H16N2O |
| Molar mass | 204.268 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Melting point | 146 to 147 °C (295 to 297 °F) |
| Boiling point | 320 °C (608 °F) |
|
|
|
|
Bufotenin (5-HO-DMT, N,N-dimethylserotonin, bufotenine) is a tryptamine related to the neurotransmitter serotonin. It is an alkaloid found in the skin of some species of toads; in mushrooms, higher plants, and mammals.
The name bufotenin originates from the Bufo genus of toads, which includes several species of psychoactive toads, most notably Incilius alvarius, that secrete bufotoxins from their parotoid glands. Bufotenin is similar in chemical structure to the psychedelics psilocin (4-HO-DMT), 5-MeO-DMT, and DMT, chemicals which also occur in some of the same fungus, plant, and animal species as bufotenin. The psychoactivity of bufotenin has been disputed, though recent studies suggest it is similar in nature to 5-MeO-DMT.
Bufotenin (bufotenine) is also known by the chemical names 5-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-HO-DMT), N,N-dimethyl-5-hydroxytryptamine, dimethyl serotonin, and mappine.
Bufotenin was first isolated from toad skin, and named by the Austrian chemist Handovsky at the University of Prague during World War I. The structure of bufotenine was first confirmed in 1934 by Heinrich Wieland’s laboratory in Munich, and the first reported synthesis of bufotenine was by Toshio Hoshino and Kenya Shimodaira in 1935.
...
Wikipedia
