Bronchi
| Bronchus | |
|---|---|
Conducting passages.
|
|

|
|
| Details | |
| System | Respiratory system |
| Artery | Bronchial artery |
| Vein | Bronchial vein |
| Nerve | Pulmonary branches of vagus nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Bronchus |
| MeSH | A04.411.125 |
| TA | A06.4.01.001 |
| FMA | 70774 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
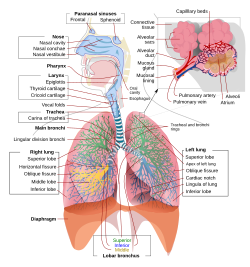
A bronchus, also known as a main or primary bronchus, is an airway in the respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. There is a right bronchus and a left bronchus and these bronchi branch into smaller secondary and tertiary bronchi which branch into smaller tubes, known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.
The trachea (windpipe) divides at the carina into two main or primary bronchi, the left bronchus and the right bronchus. The carina of the trachea is located at the level of the sternal angle and the fifth thoracic vertebra (at rest).
The right main bronchus is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the left main bronchus.It enters the right lung at approximately the fifth thoracic vertebra. The right main bronchus subdivides into three secondary bronchi (also known as lobar bronchi), which deliver oxygen to the three lobes of the right lung—the superior, middle and inferior lobe. The azygos vein arches over it from behind; and the right pulmonary artery lies at first below and then in front of it. About 2 cm from its commencement it gives off a branch to the superior lobe of the right lung, which is also called the eparterial bronchus. Eparterial refers to its position above the right pulmonary artery. The right bronchus now passes below the artery, and is known as the hyparterial branch which divides into the two lobar bronchi to the middle and lower lobes.
The left main bronchus is smaller in caliber but longer than the right, being 5 cm long. It enters the root of the left lung opposite the sixth thoracic vertebra. It passes beneath the aortic arch, crosses in front of the esophagus, the thoracic duct, and the descending aorta, and has the left pulmonary artery lying at first above, and then in front of it. The left bronchus has no eparterial branch, and therefore it has been supposed by some that there is no upper lobe to the left lung, but that the so-called upper lobe corresponds to the middle lobe of the right lung. The left main bronchus divides into two secondary or lobar bronchi to deliver air to the two lobes of the left lung—the superior and the inferior lobe.
...
Wikipedia
