Aortic arch
| Aortic arch | |
|---|---|
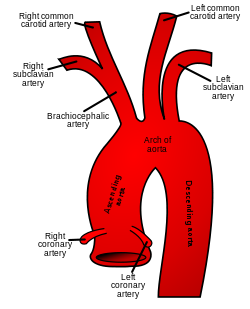
The aortic arch has three branches, the brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, and left subclavian artery.
|
|

The aortic arch and its branches shown in situ.
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | Fourth left pharyngeal arch artery |
| Source | Ascending aorta |
| Branches | Continues as descending aorta, thoracic part |
| Vein | Combination of superior and inferior vena cava |
| Supplies | From its branches, the upper body, arms, head and neck. As a part of the aorta, the entire body, with exception of the respiratory zone of the lung and the heart. |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arcus aortae |
| MeSH | A07.231.114.056.372. |
| TA | A12.2.04.001 |
| FMA | 3768 |
|
Anatomical terminology []
|
|
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta or the transverse aortic arch (English pronunciation: /eɪˈɔːrtɪk/) is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
It begins at the level of the upper border of the second sternocostal articulation of the right side, and runs at first upward, backward, and to the left in front of the trachea; then travels backward on the left side of the trachea and finally passes downward on the left side of the body of the fourth thoracic vertebra. At this point the aortic arch continues as the descending aorta.
The aortic arch has three branches. The first, and largest, branch of the arch of the aorta is the brachiocephalic trunk, which is to the right and slightly anterior to the other two branches and originates behind the manubrium of the sternum. Next, the left common carotid artery originates from the aortic arch to the left of the brachiocephalic trunk, then ascends along the left side of the trachea and through the superior mediastinum. Finally, the left subclavian artery comes off of the aortic arch to the left of the left common carotid artery and ascends, with the left common carotid, through the superior mediastinum and along the left side of the trachea. An anatomical variation is that the left vertebral artery can arise from the aortic arch instead of the left subclavian artery.
...
Wikipedia
