Bromothymol blue (data page)
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
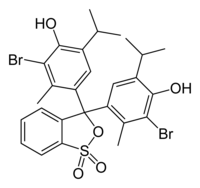
4,4′-(1,1-Dioxido-3H-2,1-benzoxathiole-3,3-diyl)bis(2-bromo-6-isopropyl-3-methylphenol)
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.884 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C27H28Br2O5S | |
| Molar mass | 624.38 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.25 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 202 °C (396 °F; 475 K) |
| Sparingly soluble in water | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.0 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet |
See: data page http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9927468 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Supplementary data page | |
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Bromothymol blue (also known as bromothymol sulfone phthalein and BTB) is a pH indicator. It is mostly used in applications that require measuring substances that would have a relatively neutral pH (near 7). A common use is for measuring the presence of carbonic acid in a liquid. It is typically sold in solid form as the sodium salt of the acid indicator.
Bromothymol blue acts as a weak acid in solution. It can thus be in protonated or deprotonated form, appearing yellow or blue, respectively. It is bright aquamarine by itself, and greenish-blue in a neutral solution. The deprotonation of the neutral form results in a highly conjugated structure, accounting for the difference in color. An intermediate of the deprotonation mechanism is responsible for the greenish color in neutral solution.
The protonated form of bromothymol blue has its peak absorption at 692 nm thus transmitting yellow light in acidic solutions, and the deprotonated form has its peak absorption at 602 nm thus transmitting blue light in more basic solutions.
The general carbon skeleton of bromothymol blue is common to many indicators including chlorophenol red, thymol blue, and bromocresol green.
The presence of one moderate electron withdrawing group (bromine atom) and two moderate donating groups (alkyl substituents) are responsible for bromothymol blue's active indication range from a pH of 6.0 to 7.6. While the conjugation is responsible for the length and nature of the color change range, these substituent groups are ultimately responsible for the indicator's active range.
Bromothymol blue is sparingly soluble in oil, but soluble in water, ether, and aqueous solutions of alkalis. It is less soluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene, toluene, and xylene, and practically insoluble in petroleum ether.
To prepare a solution for use as pH indicator, dissolve 0.10 g in 8.0 cm3 N/50 NaOH and dilute with water to 250 cm3. To prepare a solution for use as indicator in volumetric work, dissolve 0.1 g in 100 cm3 of 50% (v/v) ethanol.
...
Wikipedia

