Brodmann area 23
| Brodmann area 23 | |
|---|---|
 |
|

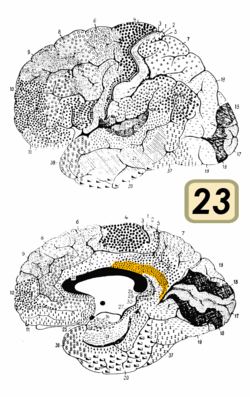
Medial surface of human brain. BA23 is shown in green.
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Area cingularis posterior ventralis |
| NeuroLex ID | Brodmann area 23 |
| FMA | 68620 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
Brodmann area 23 (BA23) is a region in the brain corresponding to some portion of the posterior cingulate cortex. It lies between Brodmann area 30 and Brodmann area 31 and is located on the medial wall of the cingulate gyrus between the callosal sulcus and the cingulate sulcus.
This area is also known as ventral posterior cingulate area 23. It is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined cingulate region of cerebral cortex. In the human it occupies most of the posterior cingulate gyrus adjacent to the corpus callosum. At the caudal extreme it is bounded approximately by the parieto-occipital sulcus. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded dorsally by the dorsal posterior cingulate area 31, rostrally by the ventral anterior cingulate area 24, and ventrorostrally in its caudal half by the retrosplenial region (Brodmann-1909).
Brodmann area 23 is a subdivision of the cerebral cortex of the guenon defined on the basis of cytoarchitecture. Brodmann regarded it as topographically and cytoarchitecturally homologous to the combined ventral posterior cingulate area 23 and dorsal posterior cingulate Brodmann area 31 of the human (Brodmann-1909). Distinctive Features (Brodmann-1905): the cortex is relatively thin; smaller cells predominate; the cell density of the multiform layer (VI) is great, producing a distinct boundary with the subcortical white matter; the internal granular layer (IV) is rather well developed; the internal pyramidal layer (V) contains a dense population of round, medium-sized ganglion cells concentrated at the border with layer IV; layers V and VI are narrow with a distinct mutual boundary.
...
Wikipedia
