White matter
| White matter | |
|---|---|
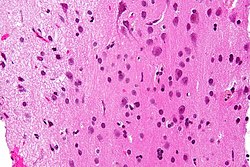
Micrograph showing white matter with its characteristic fine meshwork-like appearance (left of image - lighter shade of pink) and grey matter, with the characteristic neuronal cell bodies (right of image - dark shade of pink). HPS stain.
|
|

Human brain right dissected lateral view, showing grey matter (the darker outer parts), and white matter (the inner and prominently whiter parts).
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | substantia alba |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
White matter |
| TA | A14.1.00.009 |
| FMA | 83929 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter actively affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potentials, acting as a relay and coordinating communication between different brain regions.
White matter is named for its relatively light appearance resulting from the lipid content of myelin. However, the tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color in prepared specimens is due to its usual preservation in formaldehyde.
White matter is composed of bundles of myelinated nerve cell projections (or axons), which connect various gray matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other, and carry nerve impulses between neurons. Myelin acts as an insulator, which allows electrical signals to jump, rather than coursing through the axon, increasing the speed of transmission of all nerve signals.
The total number of long range fibers within a cerebral hemisphere is 2% of the total number of cortico-cortical fibers (across cortical areas) and is roughly the same number as those that communicate between the two hemispheres in the brain's largest white tissue structure, the Corpus callosum. Schüz and Braitenberg note "As a rough rule, the number of fibres of a certain range of lengths is inversely proportional to their length."
White matter in nonelderly adults is 1.7–3.6% blood.
...
Wikipedia
