Beta-pinene
 |
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
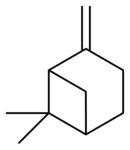
6,6-Dimethyl-2-methylenebicyclo[3.1.1]heptane
|
|||
| Other names
2(10)-Pinene; Nopinene; Pseudopinene
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.430 | ||
| KEGG | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C10H16 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.24 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.872 g/mL | ||
| Hazards | |||
| R-phrases | R10 R36 R37 R38 | ||
| S-phrases | S26 S36 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | 36 °C (97 °F; 309 K) | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
beta-Pinene (β-pinene) is a monoterpene, an organic compound found in plants. It is one of the two isomers of pinene, the other being α-pinene. It is colorless liquid soluble in alcohol, but not water. It has a woody-green pine-like smell.
This is one of the most abundant compounds released by forest trees. If oxidized in air, the allylic products of the pinocarveol and myrtenol family prevail.
Many plants from many botanical families contain the compound, including:
...
Wikipedia



