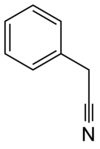
Benzyl cyanide
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
2-Phenylacetonitrile
|
|
| Other names
phenylacetonitrile, α-Tolunitrile, Benzylnitrile
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.919 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C8H7N | |
| Molar mass | 117.15 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless oily liquid |
| Density | 1.015 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −24 °C (−11 °F; 249 K) |
| Boiling point | 233 to 234 °C (451 to 453 °F; 506 to 507 K) |
| -76.87·10−6 cm3/mol | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Benzyl cyanide (abbreviated BnCN) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CN. This colorless oily aromatic liquid is an important precursor to numerous compounds in organic chemistry.
Benzyl cyanide can be produced via Kolbe nitrile synthesis between benzyl chloride and sodium cyanide and by oxidative decarboxylation of phenylalanine.
Benzyl cyanide can be hydrolyzed to give phenylacetic acid or used in the Pinner reaction to yield phenylacetic acid esters. The compound also forms an "active methylene unit" on the carbon between the aromatic ring and the nitrile functional group. This active carbon, referred to as a nitrile anion, is a useful reactive intermediate for the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds.
Benzyl cyanide is used as a solvent and as a starting material in the synthesis of fungicides, fragrances (phenethyl alcohol), antibiotics, and other pharmaceuticals. The partial hydrolysis of BnCN results in 2-phenylacetamide, a known anticonvulsant.
...
Wikipedia
