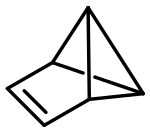
Benzvalene
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
tricyclo[3.1.0.02,6]hex-3-ene
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H6 | |
| Molar mass | 78.11 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Benzvalene is an organic compound and one of several isomers of benzene. It was first synthesized in 1971 by Thomas J. Katz et al.
The 1971 synthesis consisted of treating cyclopentadiene with methyllithium in dimethyl ether and then with dichloromethane and methyllithium in diethyl ether at −45 °C. The hydrocarbon in solution was described as having an extraordinary odor. Due to the high steric strain present in benzvalene, the pure compound easily detonates, for example by scratching.
The compound converts to benzene with a chemical half-life of approximately 10 days. This symmetry-forbidden transition is believed to take place through a diradical intermediate.
Benzvalene can be polymerized in a ROMP process to polybenzvalene. This polymer contains highly strained bicyclobutane rings which again makes it a sensitive material. The rings can be isomerized to 1,3-dienes and for this reason polybenzvalene has been investigated as a precursor to polyacetylene.
...
Wikipedia
