Barwani State
| Barwani State बरवानी रियासत |
||||||
| Princely State of British India | ||||||
|
||||||
|
||||||
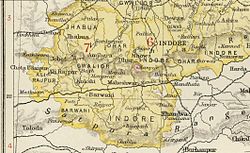
| Barwani State in the Imperial Gazetteer of India | ||||||
| History | ||||||
| • | Established | 836 | ||||
| • | Accession to the Union of India | 1948 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| • | 1941 | 3,051.02 km2(1,178 sq mi) | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| • | 1941 | 176,666 | ||||
| Density | 57.9 /km2 (150 /sq mi) | |||||
| Today part of | Madhya Pradesh, India | |||||
| Barwani Princely State | ||||||
Barwani State was a princely state in India. The seat was at Barwani.
The state was founded in the 9th century, at which time it was known as Avasgarh. Although the state lost most of its territory during the Maratha domination in the 17th century, it never became tributary to any Maratha chief.
Under the British Raj, Barwani was a state of the Bhopawar Agency, a division of the Central India Agency. The state lay in the Satpura Range south of the Narmada River. It had an area of 3,051 km2 (1,178 sq mi) and a population, in 1901, of 76,136. The inhabitants were predominantly Bhil tribals. The forests were under a British official.
After India's independence in 1948, the Rana of Barwani acceded to India, and Barwani became part of the Nimar District of Madhya Bharat state. Madhya Bharat was merged into Madhya Pradesh on 1 November 1956.
Barwani State was an 11 Gun salute state. The rulers of the State, whose title was Rana, were Rajputs of the Sesodia clan, descended from the ruling dynasty of Udaipur.
Coordinates: 22°02′N 74°54′E / 22.03°N 74.9°E
...
Wikipedia