Arsenic trifluoride
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Arsenic(III) fluoride
|
|||
| Other names
Arsenic trifluoride, trifluoroarsane
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.145 | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | CG5775000 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| AsF3 | |||
| Molar mass | 131.9168 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 2.666 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −8.5 °C (16.7 °F; 264.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 60.4 °C (140.7 °F; 333.5 K) | ||
| decomposes | |||
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, ether, benzene and ammonia solution | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Toxic, corrosive | ||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R23/25, R50/53 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S1/2), S20/21, S28, S45, S60, S61 | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
[1910.1018] TWA 0.010 mg/m3 | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca C 0.002 mg/m3 [15-minute] | ||
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [5 mg/m3 (as As)] | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
-821.3 kJ/mol | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Arsenic trifluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine with the chemical formula AsF3. It is a colorless liquid which reacts readily with water.
It can be prepared by reacting hydrogen fluoride, HF, with arsenic trioxide:
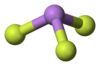
It has a pyramidal molecular structure in the gas phase which is also present in the solid. In the gas phase the As-F bond length is 170.6 pm and the F-As-F bond angle 96.2°.
Arsenic trifluoride is used as fluorinating non-metal chlorides to fluorides, in this respect it is less reactive than SbF3.
Salts containing AsF4− anion can be prepared for example CsAsF4. the potassium salt KAs2F7 prepared from KF and AsF3 contains AsF4− and AsF3 molecules with evidence of interaction between the AsF3 molecule and the anion.
AsF3 reacts with SbF5. The product obtained could be described as an ionic adduct of AsF2+ SbF6−. However, the authors conclude the formed product cannot be viewed only as an ionic compound nor entirely as a neutral adduct of AsF3SbF5. The crystal structure of formed compound displays characteristics of both an ionic pair and neutral adduct strucual motives, taking the middle ground in between both models of molecule description.
...
Wikipedia