Argentina–Chile relations
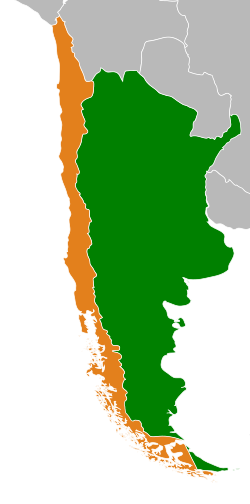 |
|
|
Argentina |
Chile |
|---|---|
Argentina–Chile relations refers to interstate relations between the Republic of Chile and the Argentine Republic. Argentina and Chile share the world's third-longest international border, which is 5,300 km (3,300 mi) long and runs from north to the south along the Andes mountains. Although gaining their independence during the South American wars of liberation, during much of the 19th and the 20th century relations between the countries were chilled as a result of disputes over the border in Patagonia. In recent years relations have improved dramatically. Despite increased trade between the two countries, Argentina and Chile have followed quite different economic policies. Chile has signed free trade agreements with countries such as China, the USA, Canada, South Korea and the EU and is an active member of the APEC, while Argentina belongs to the Mercosur regional free trade area. Both countries are members of the Union of South American Nations.
The relationship between the two countries can be traced back to an alliance during Spanish colonial times. Both colonies were offshoots of the Viceroyalty of Peru, with the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata (which Argentina was a part of) being broken off in 1776, and Chile not being broken off until independence. Argentina and Chile were colonized by different processes. Chile was conquered as a southward extension of the original conquest of Peru, while Argentina was colonized from Peru, Chile and from the Atlantic.
Argentina and Chile were close allies during the wars of independence from the Spanish Empire. Chile, like most of the revolting colonies, was defeated at a point by Spanish armies, while Argentina remained independent throughout its war of independence. After the Chilean defeat in the Disaster of Rancagua, the remnants of the Chilean Army led by Bernardo O'Higgins took refuge in Mendoza. Argentine General José de San Martín, by that time governor of the region, included the Chilean exiles in the Army of the Andes, and in 1817 led the crossing of the Andes, defeated the Spaniards, and confirmed the Chilean Independence. While he was in Santiago, Chile a cabildo abierto (open town hall meeting) offered San Martín the governorship of Chile, which he declined, in order to continue the liberating campaign in Peru.
...
Wikipedia
