Angina tonsillaris
| Tonsillitis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
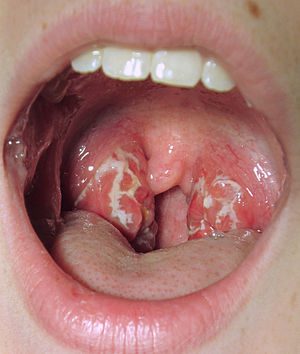
| A culture positive case of with typical tonsillar exudate | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Sore throat, fever, enlargement of the tonsils, trouble swallowing, large lymph nodes around the neck |
| Complications | Peritonsillar abscess |
| Duration | ~ 1 week |
| Causes | Viral infection, bacterial infection |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, throat swab, rapid strep test |
| Medication | Paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, penicillin |
| Frequency | 7.5% (in any given 3 months) |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, typically of rapid onset. It is a type of pharyngitis. Symptoms may include sore throat, fever, enlargement of the tonsils, trouble swallowing, and large lymph nodes around the neck. Complications include peritonsillar abscess.
Tonsillitis is most commonly caused by a viral infection, with about 5% to 40% of cases caused by a bacterial infection. When caused by the bacterium , it is referred to as strep throat. Rarely bacteria such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, or Haemophilus influenzae may be the cause. Typically the infection is spread between people through the air. A scoring system, such as the Centor score, may help separate possible causes. Confirmation may be by a throat swab or rapid strep test.
Treatment efforts involve improving symptoms and decreasing complications. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) and ibuprofen may be used to help with pain. If strep throat is present the antibiotic penicillin by mouth is generally recommended. In those who are allergic to penicillin, cephalosporins or macrolides may be used. In children with frequent episodes of tonsillitis, tonsillectomy modestly decreases the risk of future episodes.
...
Wikipedia
