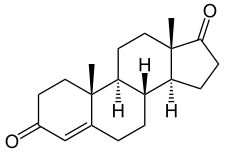
Androstendione
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | A4; Δ4-dione; Androstenedione; Androst-4-ene-3,17-dione; 4-Androstene-3,17-dione; 17-Ketotestosterone; 17-Oxotestosterone |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.504 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H26O2 |
| Molar mass | 286.4 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 173–174 °C (343–345 °F) |
|
|
|
|
Androstenedione, or 4-androstenedione (abbreviated as A4 or Δ4-dione), also known as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous weak androgen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of testosterone from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and of estrone. It is closely related to androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol).
Androstenedione is a precursor of testosterone and other androgens, as well as of estrogens like estrone, in the body. In addition to functioning as an endogenous prohormone, androstenedione also has weak androgenic activity in its own right.
Androstenedione has been found to possess some estrogenic activity, similarly to other DHEA metabolites. However, in contrast to androstenediol, its affinity for the estrogen receptors is very low, with less than 0.01% of the affinity of estradiol for both the ERα and ERβ.
In children aged 6 to 8 years old, there is a rise in androstenedione secretion along with DHEA during adrenarche. This rise in androstenedione and DHEA is hypothesized to play a crucial role for learning social, cultural and ecological skills, such as the development and understanding of sexual attraction. Furthermore, it is thought that androstenedione plays a role in levels of aggression and competition in boys, as a positive correlation between the two were observed, while testosterone levels were below detection.
Androstenedione is the common precursor of the androgen and estrogen sex hormones.
...
Wikipedia
