Ancient Roma
| Ancient Rome | |||||
| Roma | |||||
|
|||||
|
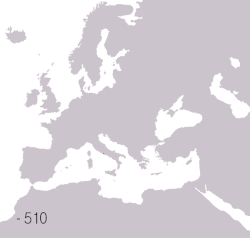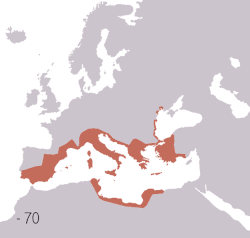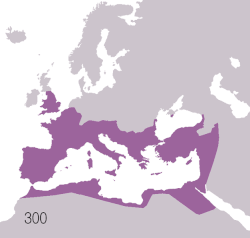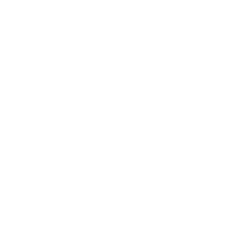
Territories of the Roman civilization:
|
|||||
| Capital | Rome | ||||
| Languages | Latin | ||||
| Government |
Kingdom (753 BC-509 BC) Republic (509 BC- 27 BC) Empire (27 BC-476 AD) |
||||
| Historical era | Ancient history | ||||
| • | Founding of Rome | 753 BC | |||
| • | Overthrow of Tarquin the Proud | 509 BC | |||
| • | Octavian proclaimed Augustus | 27 BC | |||
| • | Fall of Rome | 476 AD | |||
 |
|
|
|
Ancient Rome was an Italic civilization that began on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to become one of the largest empires in the ancient world with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants (roughly 20% of the world's population) and covering 5.0 million square kilometers at its height in AD 117.
In its approximately 12 centuries of existence, Roman civilization shifted from a monarchy to a classical republic and then to an increasingly empire. Through conquest and assimilation, it came to dominate Southern and Western Europe, Asia Minor, North Africa, and parts of Northern and Eastern Europe. Rome was preponderant throughout the Mediterranean region and was one of the most powerful entities of the ancient world. It is often grouped into classical antiquity together with ancient Greece, and their similar cultures and societies are known as the Greco-Roman world.
...
Wikipedia