ATP synthase
| ATP Synthase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
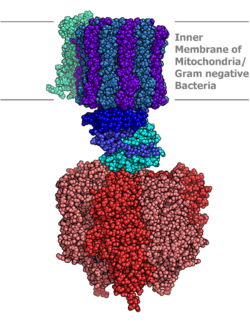
Molecular model of ATP synthase determined by X-ray crystallography
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.6.3.14 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9000-83-3 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
ATP synthase (EC 3.6.3.14) is an important enzyme that creates the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the most commonly used "energy currency" of cells for most organisms. It is formed from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi), and needs energy for its formation.
The overall reaction sequence is: ADP + Pi + Energy → ATP, where ADP and Pi are joined together by ATP synthase
Energy used is available in the form of hydrogen ions (H+
), moving down an electrochemical gradient, such as from the thylakoid lumen through the thylakoid membrane and into the chloroplast stroma (of plants) or from the inter-membrane space and into the matrix in .
Located within the thylakoid membrane and the , ATP synthase consists of two regions
The nomenclature of the enzyme has a long history. The F1 fraction derives its name from the term "Fraction 1" and FO (written as a subscript letter "o", not "zero") derives its name from being the binding fraction for oligomycin, a type of naturally-derived antibiotic that is able to inhibit the FO unit of ATP synthase. These functional regions consist of different protein subunits — refer to tables.
The F1 particle is large and can be seen in the transmission electron microscope by negative staining. These are particles of 9 nm diameter that pepper the inner mitochondrial membrane. They were originally called elementary particles and were thought to contain the entire respiratory apparatus of the mitochondrion, but, through a long series of experiments, Efraim Racker and his colleagues (who first isolated the F1 particle in 1961) were able to show that this particle is correlated with ATPase activity in uncoupled mitochondria and with the ATPase activity in created by exposing mitochondria to ultrasound. This ATPase activity was further associated with the creation of ATP by a long series of experiments in many laboratories.
...
Wikipedia
