2000 Atlantic hurricane season
| 2000 Atlantic hurricane season |
Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
June 7, 2000 |
| Last system dissipated |
October 29, 2000 |
| Strongest storm |
|
| Name |
Keith |
| • Maximum winds |
140 mph (220 km/h)
(1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure |
939 mbar (hPa; 27.73 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total depressions |
19 |
| Total storms |
15 |
| Hurricanes |
8 |
Major hurricanes
(Cat. 3+) |
3 |
| Total fatalities |
50 direct, 7 indirect |
| Total damage |
$1.2 billion (2000 USD) |
| Related articles |
|
|
Atlantic hurricane seasons
1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002
|
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 7 – June 8 |
| Peak intensity |
30 mph (45 km/h) (1-min) 1007 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 23 – June 25 |
| Peak intensity |
35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min) 1008 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 3 – August 23 |
| Peak intensity |
125 mph (205 km/h) (1-min) 950 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 8 – August 11 |
| Peak intensity |
35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min) 1009 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 13 – August 15 |
| Peak intensity |
50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) 1007 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 17 – August 19 |
| Peak intensity |
40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 1008 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 19 – August 24 |
| Peak intensity |
85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min) 991 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 1 – September 3 |
| Peak intensity |
40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 1008 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 7 – September 9 |
| Peak intensity |
35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min) 1006 mbar (hPa) |
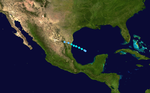
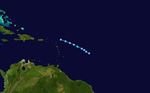
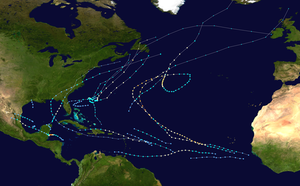
The 2000 Atlantic hurricane season was the first Atlantic hurricane season without a tropical cyclone in the month of July since 1993. The hurricane season officially began on June 1, and ended on November 30. It was slightly above average due to a La Niña weather pattern. The first cyclone, Tropical Depression One, developed in the southern Gulf of Mexico on June 7 and dissipated after an uneventful duration. However, it would be almost two months before the first named storm, Alberto, formed near Cape Verde; Alberto also dissipated with no effects on land. Several other tropical cyclones – Tropical Depression Two, Tropical Depression Four, Chris, Ernesto, Nadine, and an unnamed subtropical storm – did not impact land. Five additional storms – Tropical Depression Nine, Florence, Isaac, Joyce, and Leslie – minimally effected land areas.
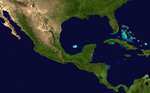
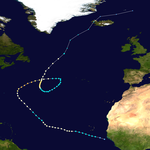
The most significant storm of the season was Hurricane Keith, which caused extensive damage in Central America. After remaining nearly stationary offshore, Keith moved inland over the Yucatan Peninsula and later made a second landfall in Mexico at hurricane intensity. It caused $319 million (2000 USD) in damage and 40 fatalities, mostly in Belize. The precursor to Tropical Storm Leslie brought severe flooding to South Florida, which losses reaching $950 million (2000 USD). Hurricane Gordon and Tropical Storm Helene both caused moderate damage in the Southeastern United States, mainly in Florida. Tropical Storm Beryl caused minor damage in Mexico and Hurricane Debby resulted in less than $1 million (2000 USD) in damage in the Greater and Lesser Antilles. Hurricane Michael brought widespread effects to Atlantic Canada, though a specific damage toll is unknown.
...
Wikipedia