1962 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1962 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
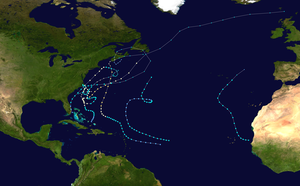
Season summary map
|
|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | August 26, 1962 |
| Last system dissipated | October 22, 1962 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Ella |
| • Maximum winds | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 950 mbar (hPa; 28.05 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 8 |
| Total storms | 5 |
| Hurricanes | 3 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) |
1 |
| Total fatalities | 29 overall |
| Total damage | $3.9 million (1962 USD) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 26 – August 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 986 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 26 – August 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 30 mph (45 km/h) (1-min) 1005 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 27 – August 31 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 1008 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 12 – September 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 20 – September 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 30 mph (45 km/h) (1-min) 1010 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 29 – October 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 mph (175 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 965 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 14 – October 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 950 mbar (hPa) |
The 1962 Atlantic hurricane season was the least active since 1939, with only five named storms. Although the season officially began on June 15, the first storm did not form until August 26. Hurricane Alma brushed the Outer Banks before becoming extratropical southeast of New England, destroying hundreds of boats and producing beneficial rainfall. In late August, Tropical Storm Becky developed unusually far east in the Atlantic Ocean, becoming the easternmost storm on record to recurve to the northeast. Celia followed in the September, forming east of the Lesser Antilles and executing a loop near Bermuda before dissipating. Hurricane Daisy was the costliest of the season, leaving about $1.1 million in damage in New England (1962 USD). The storm dropped the highest rainfall total on record in Maine, and its precipitation caused 22 traffic fatalities. The final hurricane – Ella – was also the strongest, remaining offshore of the eastern United States but causing two deaths.
In addition to the five named storms, there were three non-developing tropical depressions. The first struck Texas in August, causing street flooding and killing three. The second of three formed off the west coast of Florida and flooded widespread areas after 1 in 100 year rainfall. The floods affected 5,000 houses and caused millions in damage. The third of three non-developing storms moved across the Caribbean before striking Nicaragua in October. The season officially ended on November 15.
The hurricane season officially began on June 15, 1962. The National Hurricane Center began operations with no new equipment, and the warning agency instead opted to improve with the existing equipment. The agency had access to a system of radars that extended from Brownsville, Texas, to Eastport, Maine, which was set up in 1961. Although satellite imagery technology was available, the system was not fully active to provide daily images of Atlantic hurricanes. The season officially ended on November 15.
During the season, three hurricanes developed from five named storms. This was below the average of 10 storms per season, and represented the fewest tropical storms since 1939. Four of the five storms developed from the intertropical convergence zone. The decreased activity is partially due to the westerlies extending further south than usual, as well as a persistent ridge. In addition, temperatures in the eastern United States were cooler than usual. Activity through September 10 was the quietest in 30 years.
...
Wikipedia













