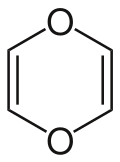
1,4-Dioxin
 |
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names
p-dioxin, dioxin
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
290-67-5 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider |
71301 |
||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 84.07 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Boiling point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | highly flammable | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related compounds
|
1,2-dioxin, dibenzodioxin |
||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
1,4-Dioxin (also referred as dioxin or p-dioxin) is a heterocyclic, organic, non-aromaticcompound with the chemical formula C4H4O2. There is an isomeric form of 1,4-dioxin, 1,2-dioxin (or o-dioxin). 1,2-Dioxin is very unstable due to its peroxide-like characteristics.
The term “dioxin” is most commonly used for a family of derivatives of dioxin, known as polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs).
1,4-Dioxin can be prepared by cycloaddition, namely by the Diels–Alder reaction of furan and maleic anhydride. The adduct formed has a carbon-carbon double bond, which is converted to an epoxide. The epoxide then undergoes a retro-Diels–Alder reaction, forming 1,4-dioxin and regenerating maleic anhydride.
The word “dioxin” can refer in a general way to compounds which have a dioxin core skeletal structure with substituent molecular groups attached to it. For example, dibenzo-1,4-dioxin is a compound whose structure consists of two benzo- groups fused onto a 1,4-dioxin ring.
...
Wikipedia



