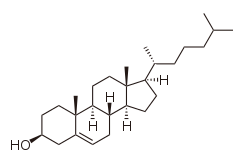
Cholesterol
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(3β)-cholest-5-en-3-ol
|
|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
2,15-dimethyl-14-(1,5-dimethylhexyl)tetracyclo[8.7.0.02,7.011,15]heptadec-7-en-5-ol
|
|
| Other names
(10R,13R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-(6-methylheptan-2-yl)-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol, Cholesterin, Cholesteryl alcohol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
57-88-5 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:16113 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL112570 |
| ChemSpider |
5775 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.321 |
| 2718 | |
| KEGG |
D00040 |
| PubChem | 5997 |
| UNII |
97C5T2UQ7J |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C27H46O | |
| Molar mass | 386.65 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.052 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 148 to 150 °C (298 to 302 °F; 421 to 423 K) |
| Boiling point | 360 °C (680 °F; 633 K) (decomposes) |
| 1.8 mg/L (30 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in acetone, benzene, chloroform, ethanol, ether, hexane, isopropyl myristate, methanol |
| -284.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 209.3 ±12.4 °C |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Cholesterol, from the Ancient Greek chole- (bile) and stereos (solid) followed by the chemical suffix -ol for an alcohol, is an organic molecule. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid molecule, and is biosynthesized by all animal cells, because it is an essential structural component of all animal cell membranes; essential to maintain both membrane structural integrity and fluidity. Cholesterol enables animal cells to dispense with a cell wall (to protect membrane integrity and cell viability), thereby allowing animal cells to change shape and animals to move (unlike bacteria and plant cells, which are restricted by their cell walls).
In addition to its importance for animal cell structure, cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones and bile acids. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as Mycoplasma, which require cholesterol for growth.
François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine".
...
Wikipedia
