Zineb
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
zinc ethane-1,2-diylbis(dithiocarbamate)
|
|
| Other names
[[1,2 ethanediylbis[dithiocarbamodithioato](2−)]] zinc,
Dithane Z-78, Aphytora, Amitan |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.970 |
| EC Number | 235-180-1 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | ZH3325000 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H6N2S4Zn | |
| Molar mass | 275.8 g/mol (monomer) |
| Appearance | pale yellow powder |
| Hazards | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
Irritants (Xi) Sensitizers |
| R-phrases | R37 R43 |
| S-phrases | (S2) S8 S24/25 S46 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
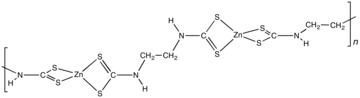
Zineb is the chemical compound with the formula {Zn[S2CN(H)CH2CH2N(H)CS2]}n. Structurally, it is classified as a coordination polymer. This pale yellow solid is used as fungicide.
It is produced by treating ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate) sodium salt, "nabam", with zinc sulfate. This procedure can be carried out by mixing nabam and zinc sulfate in a spray tank. Its uses include control of downy mildews, rusts and redfire disease. In the US it was once registered as a "General Use Pesticide", however all registrations were voluntarily cancelled following an EPA special review. It continues to be used in many other countries.
Zineb is a polymeric complex of zinc with the bis(dithiocarbamate) derived from the reaction. The polymer is composed of Zn(dithiocarbamate)2 subunits linked by ethylene backbone. A reference compound is [Zn(S2CNEt2)2]2, which features a pair of tetrahedral Zn centers bridged by one sulfur center.
...
Wikipedia
