Zeatin
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
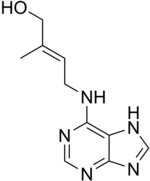
(E)-2-methyl-4-(7H-purin-6-ylamino)but-2-en-1-ol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H13N5O | |
| Molar mass | 219.25 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Off-white to yellow crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 208 to 210 °C (406 to 410 °F; 481 to 483 K) |
| Solubility in 1M NaOH | Soluble |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
2200 mg/kg (mouse, transperitoneal) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Zeatin is a plant hormone derived from adenine. Zeatin belongs to the family of plant-growth hormones called cytokinins and was discovered in immature corn kernels from the genus Zea. It promotes growth of lateral buds and when sprayed on meristems stimulates cell division to produce bushier plants.
Zeatin and its derivatives are the active ingredient in coconut milk, which causes plant growth.
Zeatin has several anti-aging effects on human skin fibroblasts.
The acute transperitoneal toxicity in mice (LD50) is 2200 mg/kg.
Zeatin has a variety of effects including:
Zeatin can also be applied to stimulate seed germination and seedling growth.
...
Wikipedia
