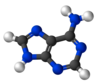
Adenine
 |
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
9H-purin-6-amine
|
|||
| Other names
6-aminopurine
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
73-24-5 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) |
Interactive image Interactive image |
||
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:16708 |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL226345 |
||
| ChemSpider |
185 |
||
| DrugBank |
DB00173 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.724 | ||
| EC Number | 200-796-1 | ||
| 4788 | |||
| KEGG |
D00034 |
||
| PubChem | 190 | ||
| RTECS number | AU6125000 | ||
| UNII |
JAC85A2161 |
||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C5H5N5 | |||
| Molar mass | 135.13 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white to light yellow, crystalline | ||
| Density | 1.6 g/cm3 (calculated) | ||
| Melting point | 360 to 365 °C (680 to 689 °F; 633 to 638 K) decomposes | ||
| 0.103 g/100 mL | |||
| Solubility | negligible in ethanol | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.15 (secondary), 9.80 (primary) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 147.0 J/(K·mol) | |||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
96.9 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | MSDS | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
227 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Adenine /ˈædᵻnᵻn/ (A, Ade) is a nucleobase (a purine derivative). Its derivatives have a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). It also has functions in protein synthesis and as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. The shape of adenine is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.
The image on the right shows pure adenine, as an independent molecule. When connected into DNA, a covalent bond is formed between deoxyribose sugar and the bottom left nitrogen, so removing the hydrogen. The remaining structure is called an adenine residue, as part of a larger molecule. Adenosine is adenine reacted with ribose as used in RNA and ATP; deoxyadenosine adenine attached to deoxyribose, as is used to form DNA.
Adenine forms several tautomers, compounds that can be rapidly interconverted and are often considered equivalent. However, in isolated conditions, i.e. in an inert gas matrix and in the gas phase, mainly the 9H-adenine tautomer is found.
...
Wikipedia