Wadi Tharthar
| Lake Tharthar | |
|---|---|
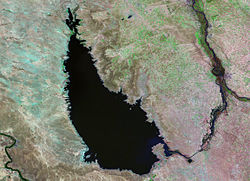
Landsat 5 (1990)
|
|
| Location | Al Anbar Province |
| Coordinates | 33°58′N 43°11′E / 33.967°N 43.183°ECoordinates: 33°58′N 43°11′E / 33.967°N 43.183°E |
| Primary inflows | Tharthar Canal |
| Primary outflows | Taksim Tharthar Canal |
| Basin countries | Iraq |
| Max. length | 120 kilometres (75 mi) |
| Max. width | 48 kilometres (30 mi) |
| Surface area | 2,710 km2 (1,050 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 40 m (130 ft) to 65 m (213 ft) |
| Water volume | 35.18 km3 (8.44 cu mi) to 85.59 km3 (20.53 cu mi) |
| Surface elevation | 3 metres (9.8 ft) |
| References | |
Lake Tharthar (also Therthar), and known in Iraq as Buhayrat ath-Tharthar (Arabic: بحيرة الثرثار), is an artificial lake opened in 1956, situated 100 kilometers northwest of Baghdad between the Tigris and the Euphrates rivers.
In 1956, the southern part of the Tharthar depression was turned into an artificial reservoir to collect flood waters of the Tigris River. The water flows via an artificial inlet canal, named Tharthar Canal. The canal diverts the access water, by means of a regulator Samarra Barrage. It merges with the lake in its southeastern bank.
The lake has an artificial outlet called Taksim Tharthar Canal, which drains to the Euphrates River directly. The canal, after 28 km from its outlet, bifurcates to another canal called "Dhira'a Dijla" (arm of tigris) that returns water back to the Tigris River.
Lake Thartar was the site of a raid in 2005 against an insurgent training base in the region.
The Tharthar depression formed During Holocene age, mainly by karstification, due to dissolving of gypsum rocks of the Fatha (nearby area) Formation. Tharthar covers roughly 2,050 square kilometres (790 sq mi), flows from the central and eastern parts of Sinjar Mountains and adjacent hills, with a floor of – 3 m, above the sea level. The maximum length and width of the depression are 120 and 48 km, respectively. The eastern rim of the depression is higher than the western one, the heights of both rims are 90 metres (300 ft) and 75 metres (246 ft), respectively.
The main purpose of the Tharthar Lake is to collect excess water of the Tigris River during flood seasons and to recharge water to the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers during dry seasons, when there is shortage of water in both rivers. Moreover, it aims in washing out the salts from the stored water, in the lake by means of natural continuous draining of the stored water.
Tharthar lake and the surrounding areas are considered one of the most important grazing areas in Iraq, including the wide wheat and corn fields covering the area. The area harbors many species of animals and vegetation.
...
Wikipedia