Visayas
| Native name: | |
|---|---|
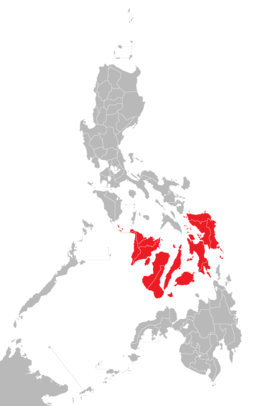
Location of the Visayas within the Philippines
|
|
| Geography | |
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Archipelago | Philippines |
| Major islands | |
| Area | 71,503 km2 (27,607 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,435 m (7,989 ft) |
| Highest point | Kanlaon Volcano |
| Administration | |
|
Philippines
|
|
| Regions | |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym |
|
| Population | 19,373,431 (2015) |
| Pop. density | 292 /km2 (756 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | |
The Visayas /vᵻˈsaɪəz/ və-SY-əz or the Visayan Islands (Visayan: Kabisay-an, local pronunciation: [kabiˈsajʔan]; Tagalog: Kabisayaan, [kabiˈsɐjaʔan]), is one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. It consists of several islands, primarily surrounding the Visayan Sea, although the Visayas are considered the northeast extremity of the entire Sulu Sea. Its inhabitants are predominantly the Visayan people.
The major islands of the Visayas are Panay, Negros, Cebu, Bohol, Leyte and Samar. The region may also include the islands of Romblon and Masbate provinces, whose populations identify as Visayan and whose languages are more closely related to Visayan languages than to the major languages of Luzon.
...
Wikipedia
