Verapamil
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /vɜːrˈæpəmɪl/ |
| Trade names | various |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 35.1% |
| Metabolism | liver |
| Biological half-life | 2.8-7.4 hours |
| Excretion | kidney: 11% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.133 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
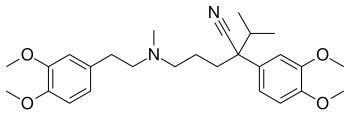
| Formula | C27H38N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 454.602 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
|
|
|
|
Verapamil, sold under various trade names, is a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure, chest pain from not enough blood flow to the heart, and supraventricular tachycardia. It may also be used for the prevention of migraines and cluster headaches. It is given by mouth or by injection into a vein.
Common side effects include headache, low blood pressure, nausea, and constipation. Other side effects include allergic reactions and muscle pains. It is not recommended in people with a slow heart rate or heart failure. It is believed to cause problems for the baby if used during pregnancy. It is in the non–dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker family of medications.
Verapamil was approved for medical use in the United States in 1981. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. Verapamil is available as a generic medication. The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 1.71 to 2.70 USD per month. In the United States a month of treatment costs 25 to 50 USD. Long acting formulations exist.
Verapamil is used for controlling ventricular rate in supraventricular tachycardia and migraine headache prevention. It is a class-IV antiarrhythmic and more effective than digoxin in controlling ventricular rate. Verapamil is not listed as a first line agent by the guidelines provided by JAMA in JNC-8. However, it may be used to treat hypertension if patient has co-morbid atrial fibrillation or other types of arrhythmia.
...
Wikipedia
