Ventral aorta
| Aorta | |
|---|---|
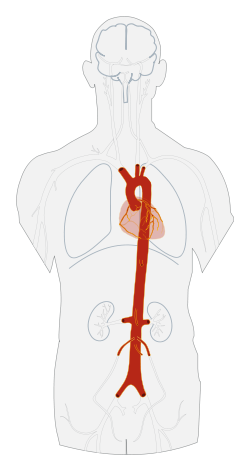
Schematic view of the aorta and a number of its most important branches
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | Truncus arteriosus Fourth left branchial artery Paired dorsal aortae (combine into the single descending aorta) |
| Source | Left ventricle |
| Branches |
Ascending aorta: Arch of aorta (supra-aortic vessels): Descending aorta, thoracic part:
Descending aorta, abdominal part:
Terminal branches: |
| Vein | Combination of coronary sinus, superior vena cava and inferior vena cava |
| Supplies | The systemic circulation (entire body with exception of the respiratory zone of the lung which is supplied by the pulmonary circulation) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Aorta, arteria maxima |
| TA | A12.2.02.001 |
| FMA | 3734 |
|
Anatomical terminology []
|
|
Ascending aorta:
Arch of aorta (supra-aortic vessels):
Descending aorta, thoracic part:
Descending aorta, abdominal part:
Terminal branches:
The aorta (/eɪˈɔːrtə/) is the main artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation.
In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections.
One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation.
Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this system, the aorta starts as the ascending aorta then travels superiorly from the heart and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch, the aorta then travels inferiorly as the descending aorta. The descending aorta has two parts. The aorta begins to descend in the thoracic cavity, and consequently is known as the thoracic aorta. After the aorta passes through the diaphragm, it is known as the abdominal aorta. The aorta ends by dividing into two major blood vessels, the common iliac arteries and a smaller midline vessel, the median sacral artery.
...
Wikipedia
