United States congressional elections, 2006
| Midterm elections | |
| Election day | November 7 |
|---|---|
| Senate elections | |
| Seats contested | 33 seats of Class I |
| Net change | Democratic +6 |
 |
|
| 2006 Senate election results map | |
| House elections | |
| Net change | Democratic +31 |
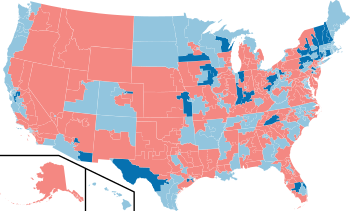 |
|
| 2006 House election results map | |
| Gubernatorial elections | |
| Seats contested | 38 (36 states, 2 territories) |
| Net change | Democratic +6 |
 |
|
| 2006 Gubernatorial election results map | |
| Legend | |
|
Democratic hold
Democratic gain
Republican hold
Independent hold
Independent gain
|
|
The 2006 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 7, 2006 in the middle of Republican President George W. Bush's second term. All United States House of Representatives seats and one third of the United States Senate seats were contested in this election, as well as 36 state and two territorial governorships, many state legislatures, four territorial legislatures and many state and local races. The election resulted in a sweeping victory for the Democratic Party which captured control of the House of Representatives, the Senate, and won a majority of governorships and state legislatures from the Republican Party.
The victory of the Democratic Party in the 2006 Congressional elections was a major milestone for an additional reason: it saw the election of the first woman to serve as the Speaker of the House. Nancy Pelosi, the leader of the Democrats in the House of Representatives, became the highest-ranking woman in the history of the government of the United States upon her election as Speaker in January 2007. In the United States, the Speaker is not only the presiding officer and leader of the majority party in the House, but the Speaker also directly follows the Vice President of the United States in the line of succession to the presidency. It was also the first election in U.S. history in which the losses for one side were so lopsided that the victorious party did not lose a single incumbent or open seat in Congress or governor's mansion.
Reasons for the Democratic party takeover include the decline of the public image of George W. Bush, the dissatisfaction of his administration's handling of both Hurricane Katrina and the War in Iraq, the beginning of the collapse of the United States housing bubble, Bush's legislative defeat regarding Social Security Privatization, and the culture of corruption, a series of scandals in 2006 involving Republican politicians.
...
Wikipedia
