Umbilical vein
| Umbilical Vein | |
|---|---|
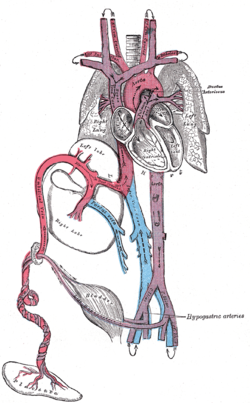
Fetal circulation; the umbilical vein is the large, red vessel at the far left.
|
|

Human embryo. Brain and heart represented from right side. Digestive tube and yolk sac in median section. (Umbilical vein labeled at bottom right.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Drains to | Internal iliac vein |
| Artery | umbilical artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena umbilicalis |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
Umbilical veins |
| TA | A12.3.12.010 |
| FMA | 70317 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The umbilical vein is a vein present during fetal development that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta into the growing fetus.
The blood pressure inside the umbilical vein is approximately 20 mmHg.
The unpaired umbilical vein carries oxygen and nutrient rich blood derived from fetal-maternal blood exchange at the chorionic villi. More than two-thirds of fetal hepatic circulation is via the main portal vein, while the remainder is shunted from the left portal vein via the ductus venosus to the inferior vena cava, eventually being delivered to the fetal right atrium.
Closure of the umbilical vein usually occurs after the umbilical arteries have closed. This prolongs the communication between the placenta and fetal heart, allowing for a sort of autotransfusion of remaining blood from the placenta to the fetus.
Within a week of birth, the neonate's umbilical vein is completely obliterated and is replaced by a fibrous cord called the round ligament of the liver (also called ligamentum teres hepatis). It extends from the umbilicus to the transverse fissure, where it joins with the falciform ligament of the liver to separate segment 4 from segments 2 and 3 of the left hepatic lobe.
Under extreme pressure, the round ligament may reopen to allow the passage of blood. Such recanalization may be evident in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Patients with cirrhosis experience rapid growth of scar tissue in and around the liver, often functionally obstructing nearby vessels. Vessel occlusion increases vascular resistance and therefore leads to hypertension. In portal hypertension, the vessels surrounding the liver are subjected to abnormally high blood pressure—so high, in fact, that the force of the blood pressing against the round ligament is sufficient to recanalize the structure. This leads to a condition called Caput medusae.
...
Wikipedia
