Umbilical artery
| Umbilical artery | |
|---|---|
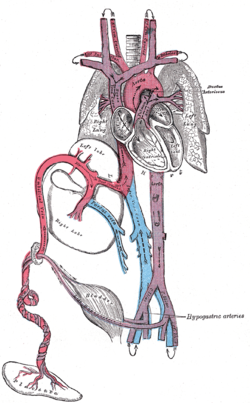
Fetal circulation; the umbilical vein is the large, red vessel at the far left. The umbilical arteries are purple and wrap around the umbilical vein.
|
|

Scheme of placental circulation.
|
|
| Details | |
| Source | internal iliac artery |
| Branches |
superior vesical artery artery of the ductus deferens |
| Vein | umbilical vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria umbilicalis |
| MeSH | A07.231.114.929 |
| Code | TE E6.0.1.3.0.0.4 |
| TA | A12.2.15.020 |
| FMA | 18820 |
|
Anatomical terminology []
|
|
The umbilical artery is a paired artery (with one for each half of the body) that is found in the abdominal and pelvic regions. In the fetus, it extends into the umbilical cord.
The umbilical arteries supply deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta. There are usually two umbilical arteries present together with one umbilical vein in the umbilical cord. The umbilical arteries surround the urinary bladder and then carry all the deoxygenated blood out of the fetus through the umbilical cord. Inside the placenta, the umbilical arteries connect with each other at a distance of approximately 5 mm from the cord insertion in what is called the Hyrtl anastomosis. Subsequently, they branch into chorionic arteries or intraplacental fetal arteries.
The umbilical arteries are actually the latter of the internal iliac arteries (anterior division of) that supply the hind limbs with blood and nutrients in the fetus.
The umbilical arteries are one of two arteries in the human body, that carry deoxygenated blood, the other being the pulmonary arteries.
The pressure inside the umbilical artery is approximately 50 mmHg.
The umbilical artery regresses after birth. A portion obliterates to become the medial umbilical ligament (be careful not to confuse this with the median umbilical ligament, a different structure that represents the remnant of the embryonic urachus). A portion remains open as a branch of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. The umbilical artery is found in the pelvis, and gives rise to the superior vesical arteries. In males, it may also give rise to the artery to the ductus deferens which can be supplied by the inferior vesical artery in some individuals.
...
Wikipedia
