Tsessebe
| Common tsessebe | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Tsessebe in Botswana | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Alcelaphinae |
| Genus: | Damaliscus |
| Species: | D. lunatus |
| Subspecies: | D. l. lunatus |
| Binomial name | |
|
Damaliscus lunatus (Burchell, 1824) |
|
| Trinomial name | |
|
Damaliscus lunatus lunatus (Burchell, 1824) |
|
 |
|
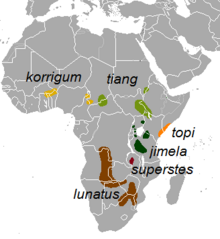
| Subspecies of Damaliscus lunatus | |
The common tsessebe or sassaby (Damaliscus lunatus lunatus) is one of five subspecies of African antelope Damaliscus lunatus of the genus Damaliscus and subfamily Alcelaphinae in the family Bovidae. It is most closely related to the topi, korrigum, coastal topi and tiang (all subspecies of Damaliscus lunatus), and the bangweulu tsessebe and bontebok in the same genus. Tsessebe are found primarily in Angola, Zambia, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Swaziland, and South Africa. Tsessebe can run at a maximum of 80 km/h.
Adult tsessebe are 150 to 230 cm in length. They are quite large animals, with males weighing 137 kg and females weighing 120 kg, on average. Their horns range from 37 cm for females to 40 cm for males. For males, horn size plays an important role in territory defense and mate attraction, although horn size is not positively correlated with territorial factors of mate selection. Their bodies are chestnut brown. The fronts of their faces and their tail tufts are black; the forelimbs and thigh are greyish or bluish-black. Their hindlimbs are brownish-yellow to yellow and their bellies are white. In the wild, tsessebe usually live a maximum of 15 years, but in some areas, their average lifespan is drastically decreased due to overhunting and the destruction of habitat.
Tsessebe are social animals. Females form herds composed of six to 10, with their young. After males turn one year of age, they are ejected from the herd and form bachelor herds that can be as large as 30 young bulls. Territorial adult bulls form herds the same size as young bulls, although the formation of adult bull herds is mainly seen in the formation of a lek. Tsessebe declare their territory through a variety of behaviors. Territorial behavior includes moving in erect posture, high-stepping, defecating in a crouch stance, ground-horning, mudpacking, shoulder-wiping, and grunting. The most important aggressive display of territorial dominance is in the horning of the ground. Another far more curious form of territory marking is through the anointing of their foreheads and horns with secretions from glands near their eyes. Tsessebe accomplish this by inserting grass stems into their preorbital glands to coat them with secretion, then waving it around, letting the secretions fall onto their heads and horns. This process is not as commonly seen as ground-horning, nor is its purpose as well known.
...
Wikipedia

