Traumatic Brain Injury
| Traumatic brain injury | |
|---|---|
 |
|
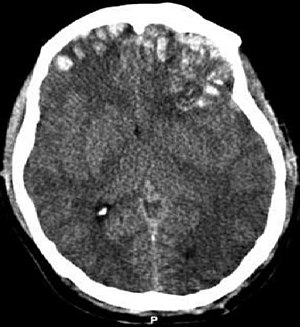
| CT scan showing cerebral contusions, hemorrhage within the hemispheres, subdural hematoma, and skull fractures | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Neurosurgery |
| ICD-10 | S06 |
| ICD-9-CM | 800.0-801.9, 803.0-804.9, 850.0-854.1 |
| DiseasesDB | 5671 |
| MedlinePlus | 000028 |
| eMedicine | med/2820 neuro/153 ped/929 |
| MeSH | D001930 |
Traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as intracranial injury, occurs when an external force injure the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism (closed or penetrating head injury), or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area). Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional, and behavioral symptoms, and outcome can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death.
Causes include falls, vehicle collisions, and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration within the cranium or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage caused at the moment of injury, a variety of events in the minutes to days following the injury may result in secondary injury. These processes include alterations in cerebral blood flow and the pressure within the skull. Some of the imaging techniques used for diagnosis include computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRIs).
Prevention measures include use of protective technology in vehicles, such as seat belts and sports or motorcycle helmets, as well as efforts to reduce the number of collisions, such as safety education programs and enforcement of traffic laws. Depending on the injury, treatment required may be minimal or may include interventions such as medications, emergency surgery or surgery years later. Physical therapy, speech therapy, recreation therapy, occupational therapy and vision therapy may be employed for rehabilitation. Counseling, supported employment, and community support services may also be useful.
...
Wikipedia
