Torreya taxifolia
| Torreya taxifolia | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Leaves of Torreya taxifolia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Cephalotaxaceae |
| Genus: | Torreya |
| Species: | T. taxifolia |
| Binomial name | |
|
Torreya taxifolia Arn. |
|
 |
|
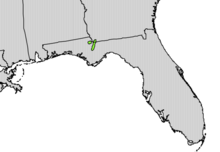
| Natural range | |
Torreya taxifolia, commonly known as the Florida nutmeg,Florida torreya, gopher wood, stinking yew, or stinking cedar (although not a true yew or cedar), is a rare and endangered tree of the yew family found in the Southeastern United States, at the state border region of northern Florida and southwestern Georgia.
It is the type species of the genus Torreya. Torreya taxifolia became one of the first federally listed endangered plant species in the United States in 1984; the IUCN lists the species as critically endangered. A survey conducted in 2000 estimated the population of T. taxifolia in its native habitat to be between 500 and 600 individuals, with approximately 10 capable of reproduction. Due to a poorly understood fungal blight that has destroyed 98% of the mature trees of the species, extinction in its native range is thought to be inevitable.
Torreya taxifolia is an evergreen tree that may reach heights of 15 to 20 meters. The trees are conical in overall shape, with whorled branches and stiff, sharp pointed, needle-like leaves 2-3.5 cm long and 3 mm broad. The male (pollen) cones are 5–7 mm long, grouped in lines along the underside of a shoot. The female (seed) cones are single or grouped two to five together on a short stem; minute at first, they mature in about 18 months to a drupe-like structure with the single large nut-like seed 2-3.5 cm long surrounded by a fleshy covering, dark green to purple at full maturity in the fall. The leaves and cones have a strongly pungent resinous odor when crushed, leading to its popular names "stinking yew" and "stinking cedar".
Torreya taxifolia is restricted to limestone bluffs and their ravines within Torreya State Park and at the Nature Conservancy Apalachicola Bluffs and Ravines Preserve, along the east bank of the Apalachicola River in the northern Florida Panhandle and immediately adjacent southernmost Georgia. Most stands are composed of immature trees of less than 2 metres (6 ft 7 in) tall.
...
Wikipedia

