Tolosa-Hunt syndrome
| Tolosa–Hunt syndrome | |
|---|---|
 |
|
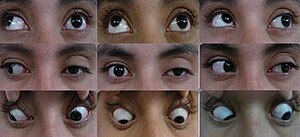
| Neuro-ophthalmologic examination showing ophthalmoplegia in a patient with Tolosa–Hunt syndrome, prior to treatment. The central image represents forward gaze, and each image around it represents gaze in that direction (for example, in the upper left image, the patient looks up and right; the left eye is unable to accomplish this movement). The examination shows ptosis of the left eyelid, exotropia (outward deviation) of the primary gaze of the left eye, and paresis (weakness) of the left third, fourth and sixth cranial nerves. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | neurology |
| ICD-10 | G44.850 |
| ICD-9-CM | 378.55 |
| DiseasesDB | 31164 |
| eMedicine | neuro/373 |
| MeSH | D020333 |
Tolosa–Hunt syndrome (THS) is a rare disorder characterized by severe and unilateral headaches with orbital pain, along with weakness and paralysis (ophthalmoplegia) of certain eye muscles (extraocular palsies).
In 2004, the International Headache Society provided a definition of the diagnostic criteria which included granuloma.
The exact cause of THS is not known, but the disorder is thought to be, and often assumed to be, associated with inflammation of the areas behind the eyes (cavernous sinus and superior orbital fissure).
Symptoms are usually limited to one side of the head, and in most cases the individual affected will experience intense, sharp pain and paralysis of muscles around the eye. Symptoms may subside without medical intervention, yet recur without a noticeable pattern.
In addition, affected individuals may experience paralysis of various facial nerves and drooping of the upper eyelid (ptosis). Other signs include double vision, fever, chronic fatigue, vertigo or arthralgia. Occasionally the patient may present with a feeling of protrusion of one or both eyeballs (exophthalmos).
THS is usually diagnosed via exclusion, and as such a vast amount of laboratory tests are required to rule out other causes of the patient's symptoms. These tests include a complete blood count, thyroid function tests and serum protein electrophoresis. Studies of cerebrospinal fluid may also be beneficial in distinguishing between THS and conditions with similar signs and symptoms.
...
Wikipedia
