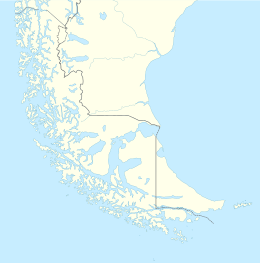
Tierra del Fuego (main island)

View of a part of Tierra del Fuego
|
|
|
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego
|
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Tierra del Fuego |
| Coordinates | 54°00′S 69°00′W / 54.000°S 69.000°WCoordinates: 54°00′S 69°00′W / 54.000°S 69.000°W |
| Archipelago | Tierra del Fuego |
| Area | 47,992 km2 (18,530 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 29th |
| Highest elevation | 2,488 m (8,163 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Darwin |
| Administration | |
| Province |
|
| Largest settlement | Río Grande (pop. 67,038) |
| Region |
|
| Largest settlement | Porvenir (pop. 4,807) |
Tierra del Fuego—literally Land of the Fire, formerly Isla de Xativa and also known as Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego—is an island near the southern tip of South America from which it is separated by the Strait of Magellan. The western portion of the island (29,484.7 km2 (11,384.1 sq mi) and 61.43% of the island) is in Chile (Province of Tierra del Fuego and Antártica Chilena Province), while the eastern portion (18,507.3 km2 (7,145.7 sq mi) and 38.57%) is in Argentina (Tierra del Fuego Province). It forms the major landmass in an extended group of islands or archipelago also known as Tierra del Fuego.
The island has an area of 47,992 km2 (18,530 sq mi), making it the 29th largest island in the world. Its two biggest towns are Ushuaia and Río Grande, both in Argentina. Other towns are Tolhuin, Porvenir, Camerón, and Cerro Sombrero. The Argentine side, Tierra del Fuego Province, has 127,205 inhabitants (2010), whereas the Chilean side, even though its area is significantly larger, has only 6,656 (2012), almost all located in the Tierra del Fuego Province.
Its highest point is Monte Darwin (2,488 m (8,163 ft)), in Chile. The northern parts of the island have oil deposits; Cerro Sombrero in Chile is the main extraction centre in the island.
...
Wikipedia