Temodar
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Temodar, Temodal, Temcad |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601250 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 15% |
| Metabolism | spontaneously hydrolyzed at physiologic pH to the active species, 3-methyl-(triazen-1-yl)imidazole-4-carboxamide (MTIC) and to temozolomide acid metabolite |
| Biological half-life | 1.8 hours |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.158.652 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
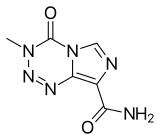
| Formula | C6H6N6O2 |
| Molar mass | 194.151 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 212 °C (414 °F) (decomp.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Temozolomide (TMZ; brand names Temodar and Temodal and Temcad) is an oral chemotherapy drug. It is an alkylating agent used as a treatment of some brain cancers; as a second-line treatment for astrocytoma and a first-line treatment for glioblastoma multiforme.
The most common side effect is bone marrow suppression. The most common non-hematological adverse effects associated with temozolomide are nausea and vomiting, which are either self-limiting or readily controlled with standard antiemetic therapy. These latter effects are usually mild to moderate (grade 1 to 2). The incidence of severe nausea and vomiting is around 4% each. Patients who have pre-existing or a history of severe vomiting may require antiemetic therapy before initiating temozolomide treatment. Temozolomide should be administered in the fasting state, at least one hour before a meal. Antiemetic therapy may be administered before, or following, administration of temozolomide. Temozolomide is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to its components or to dacarbazine. The use of temozolomide is not recommended in patients with severe myelosuppression.
Temozolomide is genotoxic, teratogenic and fetotoxic and should not be used during pregnancy. Lactating women should discontinue nursing while receiving the drug because of the risk of secretion into breast milk. One study indicated that women that have taken temozolomide without concomitant fertility preservation measures achieve pregnancy to a lesser rate later in life, but the study was too small to show statistical significance in the hypothesis that temozolomide would confer a risk of female infertility. In male patients, temozolomide can have genotoxic effects. Men are advised not to father a child during or up to six months after treatment and to seek advice on cryoconservation of sperm prior to treatment, because of the possibility of irreversible infertility due to temozolomide therapy.
...
Wikipedia
