Tebbe's reagent
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
μ-Chloro[di(cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)]dimethyl(μ-methylene)titaniumaluminum
|
|
| Other names
Tebbe reagent
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.162 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C13H18AlClTi | |
| Molar mass | 284.60 g/mol |
| Solubility in other solvents | toluene, benzene, dichloromethane, THF (low temperatures only) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
The Tebbe reagent is the organometallic compound with the formula (C5H5)2TiCH2ClAl(CH3)2. It is used in the methylenation of carbonyl compounds, that is it converts organic compounds containing the R2C=O group into the related R2C=CH2 derivative. It is a red solid that is pyrophoric in the air, and thus is typically handled with air-free techniques. It was originally synthesized by Fred Tebbe at DuPont Central Research.
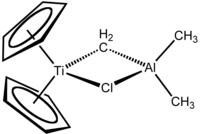
Tebbe's reagent contains two tetrahedral metal centers linked by a pair of bridging ligands. The titanium has two cyclopentadienyl ([C
5H
5]−
, or Cp) rings and aluminium has two methyl groups. The titanium and aluminium atoms are linked together by both a methylene bridge (-CH2-) and a chloride atom in a nearly square-planar (Ti–CH2–Al–Cl) geometry. The Tebbe reagent was the first reported compound where a methylene bridge connects a transition metal (Ti) and a main group metal (Al).
The Tebbe reagent is synthesized from titanocene dichloride and trimethylaluminium in toluene solution.
After about 3 days, the product is obtained after recrystallization to remove Al(CH3)2Cl. Although syntheses using the isolated Tebbe reagent give a cleaner product, successful procedures using the reagent "in situ" have been reported. Instead of isolating the Tebbe reagent, the solution is merely cooled in an ice bath or dry ice bath before adding the starting material.
...
Wikipedia
