Tāna
| Thaana (Tāna) |
|
|---|---|
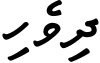 |
|
| Type |
Abugida
with no inherent vowel |
| Languages | Maldivian language |
|
Parent systems
|
|
| Direction | Right-to-left |
| ISO 15924 | Thaa, 170 |
|
Unicode alias
|
Thaana |
| U+0780–U+07BF | |
Thaana, Taana or Tāna ( ތާނަ in Tāna script) is the present writing system of the Maldivian language spoken in the Maldives. Thaana has characteristics of both an abugida (diacritic, vowel-killer strokes) and a true alphabet (all vowels are written), with consonants derived from indigenous and Arabic numerals, and vowels derived from the vowel diacritics of the Arabic abjad. Its orthography is largely phonemic.
The Thaana script first appeared in a Maldivian document towards the beginning of the 18th century in a crude initial form known as Gabulhi Thaana which was written scripta continua. This early script slowly developed, its characters slanting 45 degrees, becoming more graceful and spaces were added between words. As time went by it gradually replaced the older Dhives Akuru alphabet. The oldest written sample of the Thaana script is found in the island of Kanditheemu in Northern Miladhunmadulu Atoll. It is inscribed on the door posts of the main Hukuru Miskiy (Friday mosque) of the island and dates back to 1008 AH (AD 1599) and 1020 AH (AD 1611) when the roof of the building were built and the renewed during the reigns of Ibrahim Kalaafaan (Sultan Ibrahim III) and Hussain Faamuladeyri Kilege (Sultan Hussain II) respectively.
Thaana, like Arabic, is written right to left. It indicates vowels with diacritic marks derived from Arabic. Each letter must carry either a vowel or a sukun (which indicates "no vowel"). The only exception to this rule is nūnu which, when written without a diacritic, indicates prenasalization of a following stop.
The vowel or diacritical signs are called fili in Maldivian; there are five fili for short vowels (a, i, u, e, o), where the first two look identical to the Arabic vowel signs (fatha and kasra) and the third one (damma) looks somewhat similar. Long vowels (ā, ē, ī, ō and ū) are denoted by doubled fili (except ō, which is a modification of the short obofili).
...
Wikipedia
