Synovial fluid
| Synovial fluid | |
|---|---|
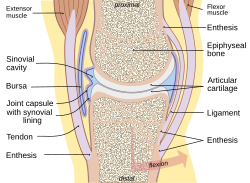
A typical joint
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | synovia |
| TA | A03.0.00.031 |
| FMA | 12277 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
Synovia, more often called synovial fluid,[help 1] is a viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints. With its egg white–like consistency, the principal role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articular cartilage of synovial joints during movement.
The inner membrane of synovial joints is called the synovial membrane and secretes synovial fluid into the joint cavity. Synovial fluid is an ultrafiltrate from plasma, and contains proteins derived from the blood plasma and proteins that are produced by cells within the joint tissues. The fluid contains hyaluronan secreted by fibroblast-like cells in the synovial membrane, lubricin (proteoglycan 4; PRG4) secreted by the surface chondrocytes of the articular cartilage and interstitial fluid filtered from the blood plasma. This fluid forms a thin layer (roughly 50 μm) at the surface of cartilage and also seeps into microcavities and irregularities in the articular cartilage surface, filling all empty space. The fluid in articular cartilage effectively serves as a synovial fluid reserve. During movement, the synovial fluid held in the cartilage is squeezed out mechanically to maintain a layer of fluid on the cartilage surface (so-called weeping lubrication). The functions of the synovial fluid include:
Synovial tissue is sterile and composed of vascularized connective tissue that lacks a basement membrane. Two cell types (type A and type B) are present: Type A is derived from blood monocytes, and it removes the wear-and-tear debris from the synovial fluid. Type B produces hyaluronan. Synovial fluid is made of hyaluronic acid and lubricin, proteinases, and collagenases. Synovial fluid exhibits non-Newtonian flow characteristics; the viscosity coefficient is not a constant and the fluid is not linearly viscous. Synovial fluid has rheopexy characteristics; viscosity increases and the fluid thickens over a period of continued stress. Normal synovial fluid contains 3–4 mg/ml hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid), a polymer of disaccharides composed of D-glucuronic acid and D-N-acetylglucosamine joined by alternating beta-1,4 and beta-1,3 glycosidic bonds. hyaluronan is synthesized by the synovial membrane and secreted into the joint cavity to increase the viscosity and elasticity of articular cartilages and to lubricate the surfaces between synovium and cartilage.
...
Wikipedia
