Swimmer's ear
| Otitis externa | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | external otitis, swimmer's ear |
 |
|
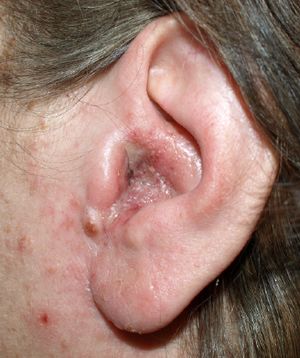
| A moderate case of otitis externa. Note the narrowing of the ear channel and the small amounts of exudate and swelling of the outer ear. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Otorhinolaryngology |
| ICD-10 | H60 |
| ICD-9-CM | 053.71, 054.73, 112.82, 380.1-380.2 |
| DiseasesDB | 9401 |
| MedlinePlus | 000622 |
| eMedicine | ped/1688 emerg/350 |
| MeSH | D010032 |
Otitis externa, also known as swimmer's ear, is an inflammation of the ear canal. It often presents with ear pain, swelling of the ear canal, and occasionally decreased hearing. Typically there is pain with movement of the outer ear. A high fever is typically not present except in severe cases.
Otitis externa may be acute (meaning less than six weeks) or chronic (meaning more than three months) in duration. Acute cases are typically due to a bacterial infection while chronic cases are often due to allergies or autoimmune disorders. Risk factors for acute cases include swimming, minor trauma from cleaning, using hearing aids or ear plugs, and other skin problems like psoriasis or dermatitis. Those with diabetes are at risk of a severe form of disease known as malignant otitis externa. Diagnosis is based on the signs and symptoms. Culturing the ear canal may be useful in chronic or severe cases.
Acetic acid ear drops may be used as a preventative measure. Treatment of acute cases is typically with antibiotic drops such as ofloxacin or acetic acid.Steroid drops may be used in addition to antibiotics. Pain medications such as ibuprofen may be used for the pain. Antibiotics by mouth are not recommended unless the person has poor immune function or there is infection of the skin around the ear. Typically improvement occurs within a day of starting treatment. Treatment of chronic cases depends on the cause.
...
Wikipedia
