Suxamethonium
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌsʌksᵻnᵻlˈkoʊlin/ |
| Trade names | Quelicin, Anectine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
intravenous, intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | NA |
| Metabolism | By pseudocholinesterase, to succinylmonocholine and choline |
| Onset of action | 30-60 sec (IV), 2-3 min (IM) |
| Duration of action | < 10 min (IV), 10-30 min (IM) |
| Excretion | Kidney (10%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
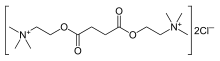
| Formula | C14H30N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 290.399 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Suxamethonium chloride, also known as suxamethonium or succinylcholine, is a medication used to cause short-term paralysis as part of general anesthesia. This is done to help with tracheal intubation or electroconvulsive therapy. It is given either by injection into a vein or muscle. When used in a vein onset of action is generally within one minute and effects last for up to 10 minutes.
Common side effects include low blood pressure, increased saliva production, muscle pain, and rash. Serious side effects include malignant hyperthermia and allergic reactions. It is not recommended in people who are at risk of high blood potassium or a history of myopathy. Use during pregnancy appears to be safe for the baby. Suxamethonium is in the neuromuscular blocker family of medications and is of the depolarizing type. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscles.
Suxamethonium was described as early as 1906 and came into medical use in 1951. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. Suxamethonium is available as a generic medication. The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 0.45 to 1.31 USD a dose. It may colloquially be referred to as "sux".
...
Wikipedia
