Strymon (river)
| Struma (Струма), Strymónas (Στρυμόνας) | |
|---|---|
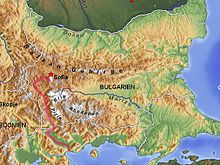
The course of the Struma in Bulgaria and Greece
|
|
| Country | Bulgaria, Greece, Macedonia, Serbia |
| Basin features | |
| Main source | The south slopes of Vitosha, Bulgaria 2,180 m (7,150 ft) |
| River mouth |
Aegean Sea, Greece 40°47′9″N 23°50′56″E / 40.78583°N 23.84889°ECoordinates: 40°47′9″N 23°50′56″E / 40.78583°N 23.84889°E |
| Basin size | 10,797 km2 (4,169 sq mi) in Bulgaria |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Length | 415 km (258 mi) |
| Discharge |
|
The Struma or Strymónas (Bulgarian Струма, pronounced [ˈstruma], Greek Στρυμόνας [striˈmonas], Turkish (Struma) Karasu 'black water') is a river in Bulgaria and Greece. Its ancient name was Strymōn (Greek: Στρυμών [stryˈmɔːn]). Its catchment area is 10,800 square kilometres (4,200 square miles). It takes its source from the Vitosha Mountain in Bulgaria, runs first westward, then southward, enters Greek territory at the Kula village. In Greece it is the main waterway feeding and exiting from Lake Kerkini, a significant centre for migratory wildfowl. The river flows into the Strymonian Gulf in Aegean Sea, near Amphipolis in the Serres regional unit. The river's length is 415 kilometres (258 miles) (of which 290 kilometres (180 mi) in Bulgaria, making it the country's fifth-longest).
Parts of the river valley belong to a Bulgarian coal-producing area, more significant in the past than nowadays. The Greek portion is a valley which is dominant in agriculture, being Greece's fourth-biggest valley. The tributaries include the Rila River, the Dragovishtitsa, the Blagoevgradska Bistritsa, the Konska River, the Sandanska Bistritsa and the Angitis.
...
Wikipedia
