Streptomycin sulfate
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
intramuscular, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability |
84% to 88% IM (est.) 0% by mouth |
| Biological half-life | 5 to 6 hours |
| Excretion | kidney |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.323 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
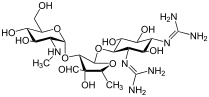
| Formula | C21H39N7O12 |
| Molar mass | 581.574 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 12 °C (54 °F) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
84% to 88% IM (est.)
Streptomycin is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, Burkholderia infection, plague, tularemia, and rat bite fever. For active tuberculosis it is often given together with isoniazid, rifampicin, and pyrazinamide. It is given by injection into a vein or muscle.
Common side effects include vertigo, vomiting, numbness of the face, fever, and rash. Use during pregnancy may result in permanent deafness in the baby. Use appears to be safe while breastfeeding. It is not recommended in people with myasthenia gravis. Streptomycin is in the aminoglycoside class of medication. It works by blocking the ability of 30S ribosomal subunits to make proteins which results in bacterial death.
Streptomycin was discovered in 1943 from Streptomyces griseus. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale cost in the developing world is between 0.38 and 4.39 USD per day. In the United States a course of treatment costs more than 200 USD.
...
Wikipedia
