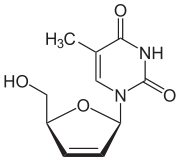
Stavudine
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Zerit |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a694033 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | >80% |
| Protein binding | Negligible |
| Metabolism | Renal elimination (~40%) |
| Biological half-life | 0.8–1.5 hours (in adults) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | 2′,3′-didehydro-2′,3′-dideoxythymidine |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.169.180 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H12N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 224.213 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Stavudine (d4T), sold under the brand name Zerit among others, is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals. It may be used for prevention after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It; however, is not a first line treatment. It is given by mouth.
Common side effects include headache, diarrhea, vomiting, rash, and peripheral nerve problems. Severe side effects include high blood lactate, pancreatitis, and an enlarged liver. It is not generally recommended in pregnancy. Stavudine is in the nucleoside analog reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) class of medication.
Stavudine was first described in 1966 and approved for use in the United States in 1994. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. It is available as a generic medication. The wholesale cost in the developing world is 1.86 to 5.40 USD per month. The World Health Organization recommends that its use be decreased due to side effects.
Stavudine is used in the treatment of HIV-1 infection, but is not a cure. It is not normally recommended as initial treatment. Stavudine can also reduce your risk of developing HIV-1 infection after coming into contact with the virus either at work (e.g., needlestick) or exposure to infected blood or other bodily fluids. It is always used in combination with other HIV medications for the better control of the infection and a reduction in HIV complications.
...
Wikipedia
