South Korean legislative election, 2012
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
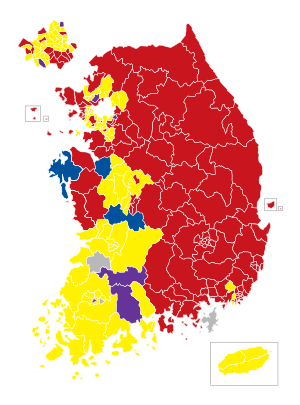
All 300 seats to the National Assembly of South Korea 151 seats needed for a majority |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 54.3% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

■ NFP ■ DUP ■ UPP ■ LFP ■ Others
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The legislative election for the 19th National Assembly was held in South Korea on 11 April 2012. The election was won by the ruling Saenuri or New Frontier Party, which renewed its majority in the National Assembly, despite losing seats. The election has been read as a bellwether for the presidential election to be held later in the year. The result confounded exit polls and media analysis which had predicted a closer outcome.
The South Korean National Assembly consists of 246 directly elected seats and 54 nationwide proportional representation seats chosen under an FPTP-PR parallel voting system. In South Korea's presidential system, the head of state chooses the cabinet, but the loss of control in the parliament could have hampered President Lee's government substantially.
Four parties won seats in the 2012 election:
Other parties that put forward candidates included the left-wing New Progressive Party and the centre-right Korea Vision Party.
The conservative parties were fragmented, particularly between Saenuri and the new KVP over the latter recruiting high-profile defected members of the incumbent party and those who were denied tickets in the election, which was also reflective of a division grew between Park's leadership and loyalists of Lee Myung-bak. However, the DUP–UPP coalition also came under strain due to irregularities in the UPP's primaries that involved co-leader Lee Jung-hee.
Campaigning for the election officially began on 29 March, though party leaders toured the country beforehand to rally support for their bids. The international media suggested that the main issues in the campaign were economic, including inflation, educational and housing costs, unemployment and underemployment, the income gap, and social welfare, while the North Korean issue did not play a role.
...
Wikipedia



