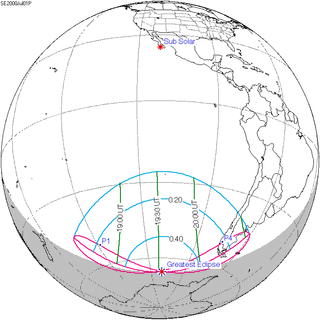
Solar eclipse of July 1, 2000
| Solar eclipse of July 1, 2000 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | -1.2821 |
| Magnitude | 0.4768 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 66°54′S 109°30′W / 66.9°S 109.5°W |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 19:33:34 |
| References | |
| Saros | 117 (68 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9509 |
A partial solar eclipse occurred on July 1, 2000. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. This eclipse occurred near the south pole, and was visible from the southern tip of South America at sunset.
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
Note: Partial solar eclipses on February 5, 2000 and July 31, 2000 occur in the previous lunar year set.
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
...
Wikipedia