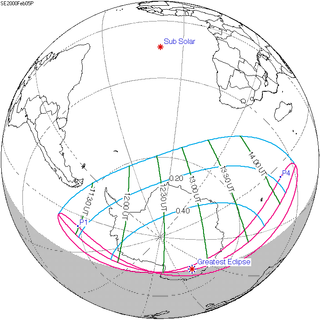
Solar eclipse of February 5, 2000
| Solar eclipse of February 5, 2000 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | -1.2233 |
| Magnitude | 0.5795 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 70°12′S 134°06′E / 70.2°S 134.1°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 12:50:27 |
| References | |
| Saros | 150 (16 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9507 |
A partial solar eclipse occurred on February 5, 2000. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. It was only visible over Antarctica.
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
...
Wikipedia