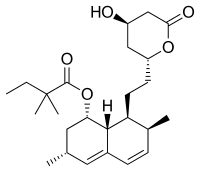
Simvastatin
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈsɪmvəstætᵻn/ |
| Trade names | Zocor, other |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a692030 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 5% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4) |
| Biological half-life | 2 hours for simvastatin and 1.9 hours for simvastatin acid |
| Excretion | Renal 13%, faecal 60% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.115.749 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H38O5 |
| Molar mass | 418.566 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Simvastatin, marketed under the trade name Zocor among others, is a lipid-lowering medication. It is used along with exercise, diet, and weight loss to decrease elevated lipid (fat) levels. It is also used to decrease the risk of heart problems in those at high risk. It is taken by mouth.
Serious side effects may include muscle breakdown, liver problems, and increased blood sugar levels. Common side effects include constipation, headaches, and nausea. A lower dose may be needed in people with kidney problems. There is evidence of harm to unborn babies when taken during pregnancy and it should not be used by those who are breastfeeding. It is in the statin class of medications and works by decreasing the manufacture of cholesterol by the liver.
Simvastatin was developed by Merck and came into medical use in 1992. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. It is available as a generic medication. The wholesale cost in the developing world is 0.01 to 0.12 USD per day as of 2014[update]. In the United States it costs between 0.50 and 1.00 USD per day. Simvastatin is made from the fungus Aspergillus terreus.
The primary uses of simvastatin are to treat dyslipidemia and to prevent atherosclerosis-related complications such as stroke and heart attacks in those who are at high risk. It is recommended to be used as an addition to a low cholesterol diet.
In the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial of 5 years duration), simvastatin reduced overall mortality in people with existing cardiovascular disease and high LDL cholesterol by 30% and reduced cardiovascular mortality by 42%. The risks of heart attack, stroke, or needing a coronary revascularization procedure were reduced by 37%, 28%, and 37% respectively.
...
Wikipedia
