Siberian tigers
| Siberian tiger Temporal range: Holocene |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Male at the Leipzig Zoological Garden | |
 |
|
| Female | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Pantherinae |
| Genus: | Panthera |
| Species: | P. tigris |
| Subspecies: | P. t. tigris |
| Trinomial name | |
|
Panthera tigris tigris (Linnaeus, 1758) |
|
 |
|
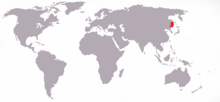
| Distribution of the Siberian tiger (in red) | |
| Synonyms | |
|
formerly:
|
|
formerly:
The Siberian tiger (Panthera tigris tigris), also called Amur tiger, is a tiger population inhabiting mainly the Sikhote Alin mountain region in southwest Primorye Province in the Russian Far East. The Siberian tiger once ranged throughout Korea, Northeast China, Russian Far East, and eastern Mongolia. In 2005, there were 331–393 adult and subadult Siberian tigers in this region, with a breeding adult population of about 250 individuals. The population had been stable for more than a decade due to intensive conservation efforts, but partial surveys conducted after 2005 indicate that the Russian tiger population was declining. An initial census held in 2015 indicated that the Siberian tiger population had increased to 480–540 individuals in the Russian Far East, including 100 cubs. This was followed up by a more detailed census which revealed there was a total population of 562 wild Siberian tigers in Russia.
Results of a phylogeographic study comparing from Caspian tigers and living tiger subspecies indicate that the common ancestor of the Siberian and Caspian tigers colonized Central Asia from eastern China, via the Gansu−Silk Road corridor, and then subsequently traversed Siberia eastward to establish the Amur tiger population in the Russian Far East. The Caspian and Siberian tiger populations were the northernmost in mainland Asia.
The Siberian tiger was also called Manchurian tiger, Korean tiger, and Ussurian tiger, depending on the region where individuals were observed.
The tiger is reddish-rusty, or rusty-yellow in colour, with narrow black transverse stripes. The body length is not less than 150 cm (60 in), condylobasal length of skull 250 mm (10 in), zygomatic width 180 mm (7 in), and length of upper carnassial tooth over 26 mm (1 in) long. It has an extended supple body standing on rather short legs with a fairly long tail.
...
Wikipedia

