Sevelamer
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Renagel, Renvela |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601248 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 0% |
| Excretion | faecal 100% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.207.865 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
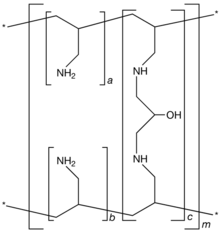
| Formula | [(C3H7N)a+b.(C9H17N2O)c]m where a+b:c = 9:1 |
| Molar mass | variable |
|
|
|
Sevelamer (rINN) (/sɛˈvɛləmər/ or /sɛˈvɛləmɪər/) is a phosphate binding drug used to treat hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. When taken with meals, it binds to dietary phosphate and prevents its absorption. Sevelamer was invented and developed by GelTex Pharmaceuticals. Sevelamer is currently marketed by Sanofi under the trade names Renagel (sevelamer hydrochloride) and Renvela (sevelamer carbonate).
Sevelamer consists of polyallylamine that is crosslinked with epichlorohydrin. The marketed form sevelamer hydrochloride is a partial hydrochloride salt being present as approximately 40% amine hydrochloride and 60% sevelamer base. The amine groups of sevelamer become partially protonated in the intestine and interact with phosphate ions through ionic and hydrogen bonding.
Sevelamer is used in the management of hyperphosphatemia in adult patients with stage 4 and 5 chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis. Its efficacy at lowering phosphate levels is similar to that of calcium acetate, but without the accompanying risk of hypercalcemia.
...
Wikipedia
